Feline Chronic Gingivostomatitis (FCGS)
At Eastcott Referrals, our Dentistry, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (DOMS) team understands the significant challenges faced by cats living with Feline Chronic Gingivostomatitis (FCGS). This debilitating condition causes intense inflammation and pain within the mouth, often affecting a cat’s ability to eat, groom and enjoy life. Through expert diagnosis, advanced treatment techniques and compassionate aftercare, we are committed to improving the comfort and wellbeing of affected patients.
What is FCGS?
FCGS is a severe inflammatory disease involving the soft tissues of the mouth, particularly the gums, back of the mouth and surface of the tongue. While the exact cause remains unclear, it is widely believed that the condition is the result of an abnormal immune response toward the normal plaque bacteria found on the tooth’s surface. Likely contributing or triggering factors include chronic viral infections, dental plaque and individual immune system differences.
The result is often severe painful due to the widespread inflammation, that can significantly impact a cat’s health and quality of life.
Recognising the Signs
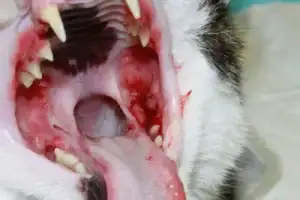
This images shows the intense oral inflammation and ulceration, especially of the back of the mouth, so common in FCGS. Note that the teeth have little plaque and calculus
Cats affected by FCGS often show a range of symptoms, many of which are linked to oral discomfort and pain:
- Reluctance or refusal to eat, particularly dry food
- Excessive drooling, sometimes with traces of blood
- Noticeably bad breath (halitosis)
- Weight loss and reduced body condition
- Decreased grooming behaviour
- Irritability or withdrawal due to persistent pain
As the disease progresses, even routine activities such as eating and cleaning themselves can become difficult or distressing.
How We Diagnose FCGS
Our approach to diagnosis at Eastcott is thorough and gentle, taking into account the sensitivity of affected patients. Steps typically include:
- A full oral examination, often carried out under general anaesthesia to ensure minimal stress and allow a detailed assessment
- Dental radiographs to examine the roots, bone structures and any concurrent dental disease
- Laboratory testing to investigate possible underlying health issues such as viral infections and systemic diseases such as kidney damage or diabetes.
- Biopsy in selected cases, where confirmation of the diagnosis or exclusion of other conditions is necessary
This careful diagnostic process helps us form a clear picture of the disease severity and guides our treatment planning.
Treatment Options
Managing FCGS requires a tailored and often multi-faceted approach. Our priority is to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation and, where possible, tackle the underlying cause.
Dental Extractions
Surgical removal of teeth is often the most effective treatment option for long-term improvement:
- Partial-mouth extractions (removing premolars and molars) may be recommended initially
- Full-mouth extractions may be advised for more severe or unresponsive cases
Removing teeth reduces plaque and bacteria, which in turn helps decrease the immune system’s overreaction.
Medical Support
Although extractions can dramatically improve many cases, additional medical management may also be necessary, including:
- Anti-inflammatory medication to reduce discomfort and swelling
- Immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory drugs to control the immune response
- Pain relief tailored to the individual patient’s needs
- Antibiotics in cases where secondary infection is present
In particularly challenging or refractory cases, newer therapies may also be considered to help manage the disease, such as stem cell transfusions.
Supporting Recovery and Long-Term Management
FCGS is often a chronic condition, which means ongoing care is important. Our aftercare support includes:
- Post-operative pain management to ensure comfort during recovery
- Dietary advice, often recommending soft or palatable food to encourage eating
- Tailored home care guidance, including advice for monitoring and recognising any flare-ups
- Scheduled re-examinations to assess healing and track progress
Our commitment extends beyond initial treatment, providing support for both referring vets and owners throughout the pet’s journey.
Referring a Case to Eastcott Referrals
Feline Chronic Gingivostomatitis can be a distressing and frustrating condition to manage without specialist input. At Eastcott, our Dentistry, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery team is equipped with the expertise, facilities and compassion needed to help cats with FCGS lead more comfortable lives.
Veterinary professionals can refer cases to our team using our straightforward online referral process. We also welcome enquiries and discussions prior to referral should advice be needed.
Together with our referring colleagues, we are committed to delivering exceptional care to every patient.
